Introduction
- Sometimes it is called spark machining, spark eroding, burning, die sinking or wire erosion
- In there a desired shape is obtained using electrical discharges (sparks).
- Material is removed from the work-piece by a series of current discharges between two electrodes, separated by a dielectric liquid and subject to an electric voltage.
- One electrodes – ‘tool-electrode’ or ‘tool’ or ‘electrode’.
- Other electrode - work-piece-electrode or ‘work-piece’.
General Aspects Of EDM
EDM is a machining a hard metals or those that would be very difficult to machine with traditional techniques.
- EDM works with materials that are electrically conductive, although methods for machining insulating ceramics with EDM have been proposed.
- EDM can cut contours or cavities in hardened steel without the need for heat treatment to soften and re-harden them.
- Same method can be used with any other metal or metal alloy such as titanium, hastelloy, kovar, and inconel.
- Applications of this process to shape poly-crystalline diamond tools have been reported
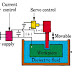
EDM-System
EDM-Component
- Electric current
- Dielectric medium
- Work-piece and tool
- Servo moter
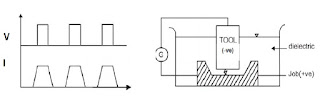
- Work-piece & tool are electrically connected to a DC power supply.
- The density of current in the discharge of the channel is of the order of 10000 A/cm2 and power density is nearly 500 MW/cm2.
- The range of spark gap is from 0.005 mm to 0.05 mm is maintained between the work piece and the tool.
Working Principle & How its Work
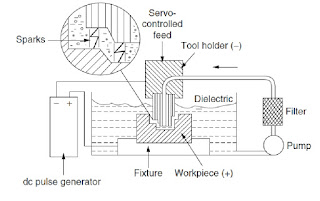
- Metal removal based on the principle of material removal by an interrupted electric spark discharge between the electrode tool and the work piece.
- Tool and work material are be conductors.
- Tool and work material are present in a dielectric medium.
- Kerosene or deionised water is used as the dielectric medium.
- Gap is establish between the tool and the work-piece.
- Gap between the tool and work-piece, an electric field would be established.
- Mostly tool is connected to the negative terminal (cathode) of the generator and the work-piece is connected to positive terminal (anode).
- When electric field is established between the tool and the job, the free electrons on the tool are subjected to electrostatic forces.
- When bonding energy of the electrons is less, electrons would be emitted from the tool.
- Emission of electrons are called or termed as ‘cold emission’.
- “cold emitted” electrons are then accelerated towards the job through the dielectric medium.
- Electron gain velocity and energy, and start moving towards the job, there would be collisions between the electrons and dielectric molecules.
- Electron will be collision and may result in ionization of the dielectric molecule.
- When electrons get accelerated, more positive ions and electrons would get generated due to collisions.
- This process will increase the concentration of electrons and ions in the dielectric medium between the tool and the job at the spark gap.
- Concentration would be so high that the matter existing in that channel could be characterise as “plasma”.
- A large number of electrons will flow from tool to job and ions from job to tool.
- This is called avalanche motion of electrons.
- The movement of electrons and ions can be visually seen as a spark.
- The electrical energy is dissolute as the thermal energy of the spark.
- And the high speed electrons then impinge on the job and ions on the tool.
- The Kinetic energy of the electrons and ions on impact with the surface of the job and tool respectively would be converted into thermal energy or heat flux.
- Temperature which would be in excess of 10,000oC.
- Rise in temperature leads to material removal.
EDM-Working Principle
- Withdrawal of potential difference, plasma channel collapses.
- This creates compression shock waves on both the electrode surface.
- At high spots on work piece surface, which are closest to the tool.
- This molten material and forms a crater around the site of the spark.
EDM - Schematic
EDM-Working Principle
EDM-Electrode Material
- When Electrode material is impinged by positive ions then it would not undergo much tool wear.
- The tool should be easily workable.
Characteristics Of Electrode Material
- Higher density
- High melting point
- Easy manufacturability
- Cost – cheap
- High electrical conductivity
- High thermal conductivity
Used Commonly In The Industry
The different electrode materials which are used commonly in the industry:
- Graphite
- Electrolytic oxygen free copper
- Tellurium copper – 99% Cu + 0.5% tellurium
- Brass
Function Of Dielectric
There are three important functions of a dielectric medium.- The gap will be Insulates between the tool and work.
- Cools the electrode.
- Flush metal particles out of the working gap.
EDM-Flushing
- Flushing is a process of introducing clean filtered dielectric fluid into spark gap
- One of the important factors is the removal of debris (chips) from the working gap.
- Flushing the work material particles out of the working gap is very important, to prevent them from forming bridges that cause short circuits.
- If flushing is not applied properly, it can result in erratic cutting and poor machining conditions.
- Flushing of dielectric plays a major role in the maintenance of stable machining.
Normal flow (Majority)
- Dielectric is under pressure, through one or more passages in the tool and is forced to flow through the gap between tool and work.
- Flushing generally placed in those areas where the cuts are deepest.
- Sometimes normal flow is undesirable because it produces a tapered opening in the work-piece.
Reverse flow
- It is useful in machining deep cavity dies, where the taper produced using the normal flow mode can be reduced.
- Fluid flowing between the work-piece and the tool, there is no side sparking and, therefore, no taper is produced.
Jet flushing
- Machining of desire work-piece can be achieved by using a spray or jet of fluid directed against the machining gap.
- The time of machining is always longer with jet flushing than with the normal and reverse flow modes.
Immersion flushing
- Simple immersion of the discharge gap is sufficient.
- Debris removal can be enhanced during immersion cutting by providing relative motion between the tool and work-piece.
- Cycle interruption comprises periodic reciprocation of the tool relative to the work-piece to effect a pumping action of the dielectric.
Application-EDM Drilling
Uses of tool electrode where the dielectric is flushed.
- Whenever solid rods are used; dielectric is fed to the machining zone by either suction or injection through pre-drilled holes.
- Tapered, curved can be produced by EDM.
- Creating cooling channels in turbine blades made of hard alloys is a typical application of EDM drilling.
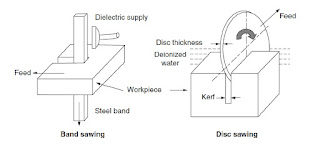
Application-Wdm Sawing
- Tool cuts at a rate that is twice that of the conventional abrasive sawing method.
- Cutting of billets and bars - has a smaller kerf & free from burrs.
- Fine finish of 6.3 to 10 μm with a recast layer of 0.025 to 0.130 mm
Application-Machining Of Spheres
- Coworkers (1995) used simple tubular electrodes in EDM machining of spheres, to a dimensional accuracy of ±1 μm and Ra < 0.1 μm.
- Spherical shapes in conducting ceramics using the tool and workpiece arrangement as shown below, can be machining by rotary EDM.
Application-Machining Of Dies
- EDM milling uses standard cylindrical electrodes.
- Simple-shaped electrode (Fig. 1) is rotated at high speeds and follows specified paths in the workpiece like the conventional end mills.
- Makes EDM very versatile like mechanical milling process.
- Complex-shaped electrodes for die sinking (Fig. 2) of three-dimensional cavities.
- Dielectric flushing due to high-speed electrode rotation.
- Electrode wear can be optimized due to contouring motions.
- Main limitation in EDM milling - Complex shapes with sharp corners cannot be machined because of the rotating tool electrode.
- EDM milling replaces conventional die making that requires variety of machines such as milling, wire cutting, and EDM die sinking machines.
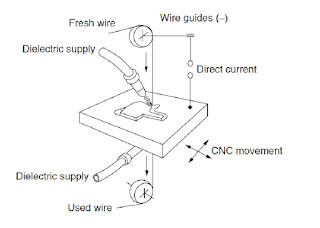
Application-Wire EDM
- Uses a continuously moving conductive wire electrode.
- Spark erosion as the wire electrode is fed, from a fresh wire spool, through the work-piece causes to material removel.
- Horizontal movement of the worktable (CNC) determines the path of the cut.
- During the machining of superhard materials like polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and cubic boron nitride (CBN) blanks, and other composites.
- In (1995) used wire EDM for accurately shaping these materials, without distortion or burrs
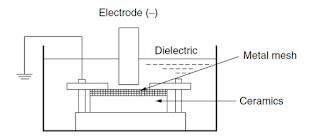
Application-EDM Of Insulators
Electrical Discharge Machine: Principle,Component
 Reviewed by Anjum Rana
on
March 06, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Anjum Rana
on
March 06, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Anjum Rana
on
March 06, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Anjum Rana
on
March 06, 2019
Rating:












No comments: